close()를 사용해 직접 닫아줘야하는 자바 자원 : InputStream OutputStream, java.sql.Connection
1. 자원이 닫힘을 보장하는 수단 try-finally의 단점
- 코드 가독성에있어서 지저분하다.
- 두번째 예외가 첫번째 예외를 집어삼켜버려 실제 시스템에서 디버깅을 어렵게 한다.
static void copy(String src, String dst) throws IOException{
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
try{
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dst);
try{
byte[] buf = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int n;
while ((n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
}finally{
out.close();
}
}finally{
in.close();
}
}firstLineOfFile 메서드안의 readLine 메서드가 예외 > close 메서드 실패 > 두번째 예외가 첫번째 예외를 집어삼킨다.
2. 자원 회수의 최선책 try-with-resources
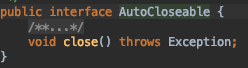
AutoCloseable 인터페이스 구현 : close() 메서드 하나만 정의하였다.
static void copy(String src, String dst) throws IOException {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dst)) {
byte[] buf = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
int n;
while ((n = in.read(buf)) >= 0)
out.write(buf, 0, n);
} catch (IOException e) {
return defaultVal;
}
}- 읽기 쉽고 문제 진단에 유리하다.
- catch를 이용해 try문을 중첩하지 않고도 다수의 예외 처리가 가능하다.
- 숨겨진 예외도 버려지지 않고, suppressed 꼬리표를 달고 출력된다.
readLine()과 close() 호출 양쪽에서 예외가 발생하면, close() 예외는 숨겨지고 readLine()에서 발생한 예외가 기록된다.
'Dev Book Review > Effective Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Effective Java] item10. equals는 일반 규약을 지켜 재 정의하라 (0) | 2020.04.19 |
|---|---|
| [Effective Java] Chapter 2 Summary : 객체 생성과 파괴 (0) | 2020.04.15 |
| [Effective Java] item8. finalizer와 cleaner 사용을 피해라 (0) | 2020.04.15 |
| [Effective Java] item7. 다 쓴 객체 참조를 해제하라 (0) | 2020.04.15 |
| [Effective Java] item6. 불필요한 객체 생성을 피하라 (0) | 2020.04.15 |



